Paper | Code | Model | Data | Base Model
Overview
LLaVA-OneVision-1.5-RL presents an RL post-training stage utilizing 67K curated examples with discrepancy-based selection to generate explicit chain-of-thought reasoning, achieving significant performance gains on STEM, coding, and reasoning benchmarks while maintaining visual understanding capabilities.
Our contributions are threefold:
(1) Discrepancy-Driven Data Curation. We identify tasks where model performance gap exists between Pass@N and Pass@1 metrics, targeting “latent capability” rather than knowledge injection.
(2) Rule-Based Reward System. We employ domain-specific verification rules rather than learned preference models, enabling precise feedback across STEM, grounding, spatial reasoning, counting, coding, OCR, and diagram tasks.
(3) Two-Stage Curriculum Training. We design a training curriculum that first stabilizes concise task performance with answer-only RL, then unlocks deeper reasoning through chain-of-thought RL.
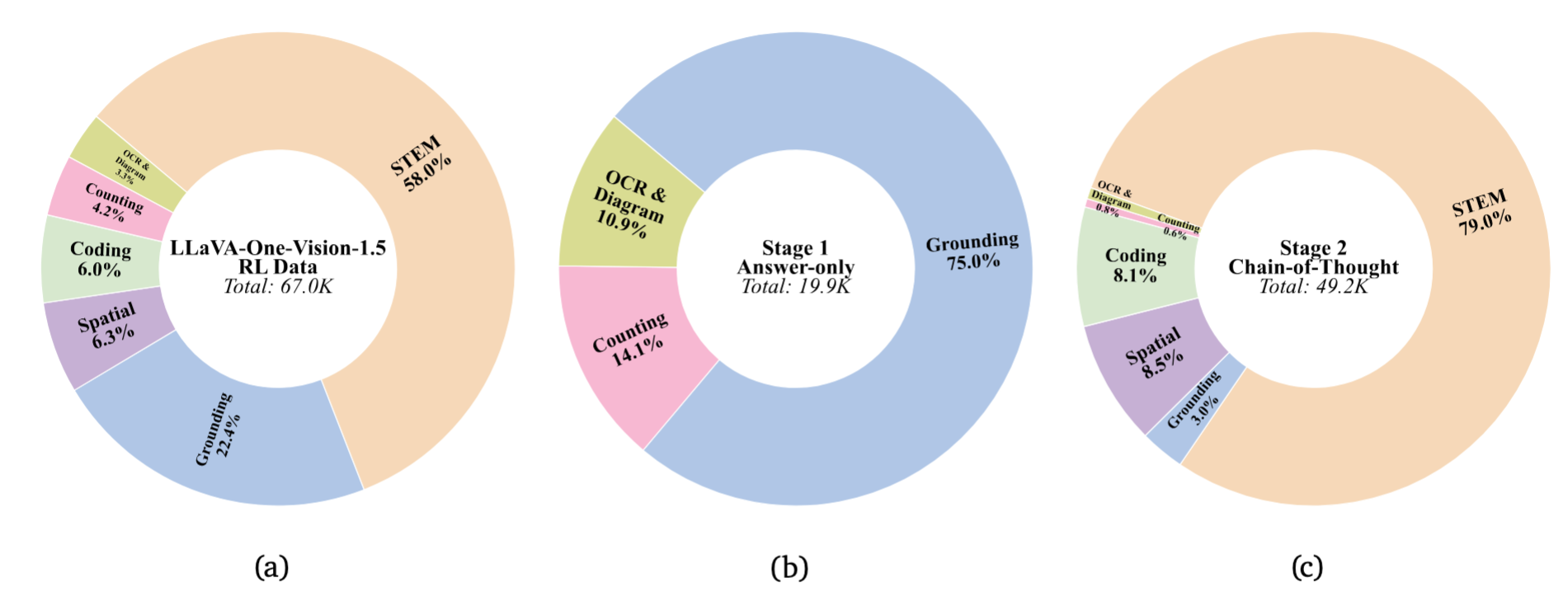
RL Data Strategy
Discrepancy-Driven Selection
We identify tasks where model performance gap exists between Pass@N and Pass@1 metrics. This approach targets “latent capability” rather than knowledge injection, ensuring the model learns to better utilize its existing knowledge.
Reward-Based Sampling
Multiple candidate responses are filtered by average reward scores to exclude trivial and unsolvable cases, focusing on medium-difficulty instances that provide optimal learning signals.
Reward System Architecture
We employ a rule-based paradigm with domain-specific verification rules rather than learned preference models:
| Category | Source | Reward Design |
|---|---|---|
| STEM | ViRL39K | Choice accuracy & math expression equivalence |
| Grounding | Ref-L4, VigoRL-SA | IoU between predicted/reference boxes; choice accuracy |
| Spatial | VigoRL-SAT | Choice accuracy |
| Counting | PixmoCount | Numeric token equivalence |
| Coding | WebCode2M, UniSVG | Token/tag overlap; SVG rendering similarity [0,1] |
| OCR | InfoVQA | Text similarity |
| Diagram | AI2D | Choice accuracy |
Two-Stage Training Procedure
Training uses Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) within the AReaL asynchronous framework:
Stage 1: Answer-only RL
Normal split training with instruction “Put ONLY your final answer within <answer></answer>.” This stage stabilizes concise task performance.
Stage 2: Chain-of-Thought RL
Long-reasoning data with instruction “Think and solve… within <think></think>…” This stage unlocks deeper reasoning capabilities. A small proportion of normal-set examples are interspersed to prevent forgetting perception skills.
Performance Results
Core Capability Enhancement
General VQA Benchmarks (Average +1.0):
| Benchmark | Base | +RL |
|---|---|---|
| MMStar | 67.7 | 68.2 |
| MMBench (EN) | 84.1 | 85.7 |
| MMBench (CN) | 81.0 | 84.2 |
| MME-RealWorld (EN) | 61.7 | 63.4 |
| CV-Bench | 80.7 | 82.9 |
| RealWorldQA | 68.1 | 68.4 |
Reasoning Tasks (Average +6.0):
| Benchmark | Base | +RL | Δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| MathVista Mini | 69.6 | 72.3 | +2.7 |
| WeMath | 61.5 | 69.4 | +7.9 |
| MathVision | 25.6 | 34.4 | +8.8 |
| MMMU Validation | 55.4 | 58.8 | +3.4 |
| MMMU-Pro | 25.2 | 35.7 | +10.5 |
OCR & Chart (Average +0.0):
| Benchmark | Base | +RL |
|---|---|---|
| ChartQA | 86.5 | 87.4 |
| DocVQA | 95.0 | 91.9 |
| InfoVQA | 78.4 | 76.6 |
Extended Capability Analysis
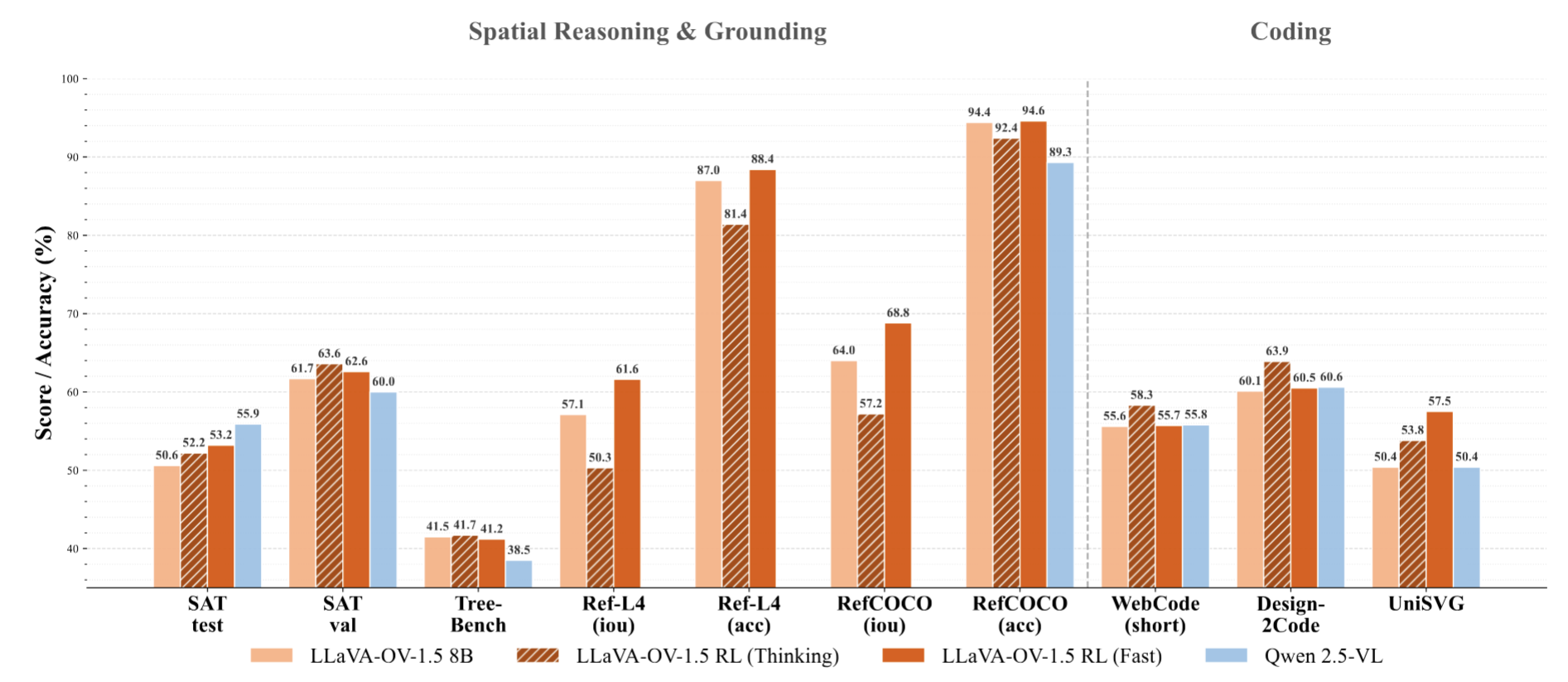
Spatial & Grounding: RL “fast mode” significantly enhances fine-grained perception on SAT and Ref-L4 benchmarks.
Coding: “Thinking” mode achieves highest scores on Design2Code and UniSVG, demonstrating chain-of-thought benefits for structural code generation.
Development Roadmap
This release represents Stage 3 in a multi-phase project:
| Stage | Focus | Data Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 & 1.5 | Pre-training & Mid-training | 85M multimodal samples |
| Stage 2 | Visual instruction tuning (SFT) | 22M instruction-following samples |
| Stage 3 (Current) | RL post-training with GRPO | 67K curated samples |
Acknowledgements
We thank the following projects and frameworks:
- AReaL: Lightning-Fast RL for LLM Reasoning and Agents
- sglang: Fast serving framework for LLMs and vision language models
- lmms-eval: Standardized evaluation framework
- LLaVA: Large Language-and-Vision Assistant
- LLaVA-NeXT: Next-generation multi-modal assistant


