Overview
Our contributions are threefold:
(1) High-quality multimodal reasoning data curation.
We provide the first systematic study on constructing SFT and RL datasets for multimodal reasoning, showing that both source diversity and answer diversity are crucial for building reliable supervision signals.
(2) A strong and reproducible SFT recipe.
We introduce a robust SFT pipeline with step-by-step validation, careful teacher-model selection, and cross-domain data integration, enabling the construction of a high-quality cold-start reasoning dataset.
(3) An advanced RL training recipe.
Through an extensive comparison of GSPO, GRPO, and DAPO, we identify the most stable and scalable RL strategy and build a reliable RL pipeline that significantly strengthens multimodal reasoning performance.

Performance Comparison with State-of-the-Art Large Multimodal Reasoning Models across Various Benchmarks. Our proposed OpenMMReasoner consistently outperforms competing methods, highlighting its effectiveness in complex reasoning tasks.
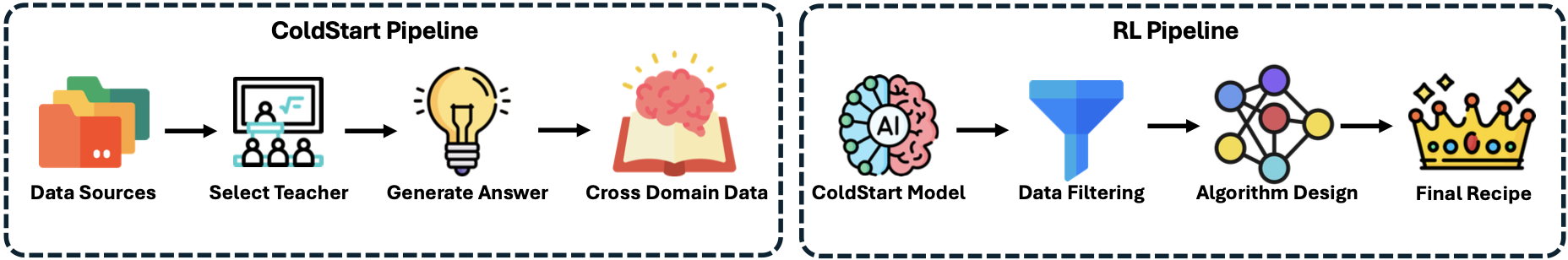
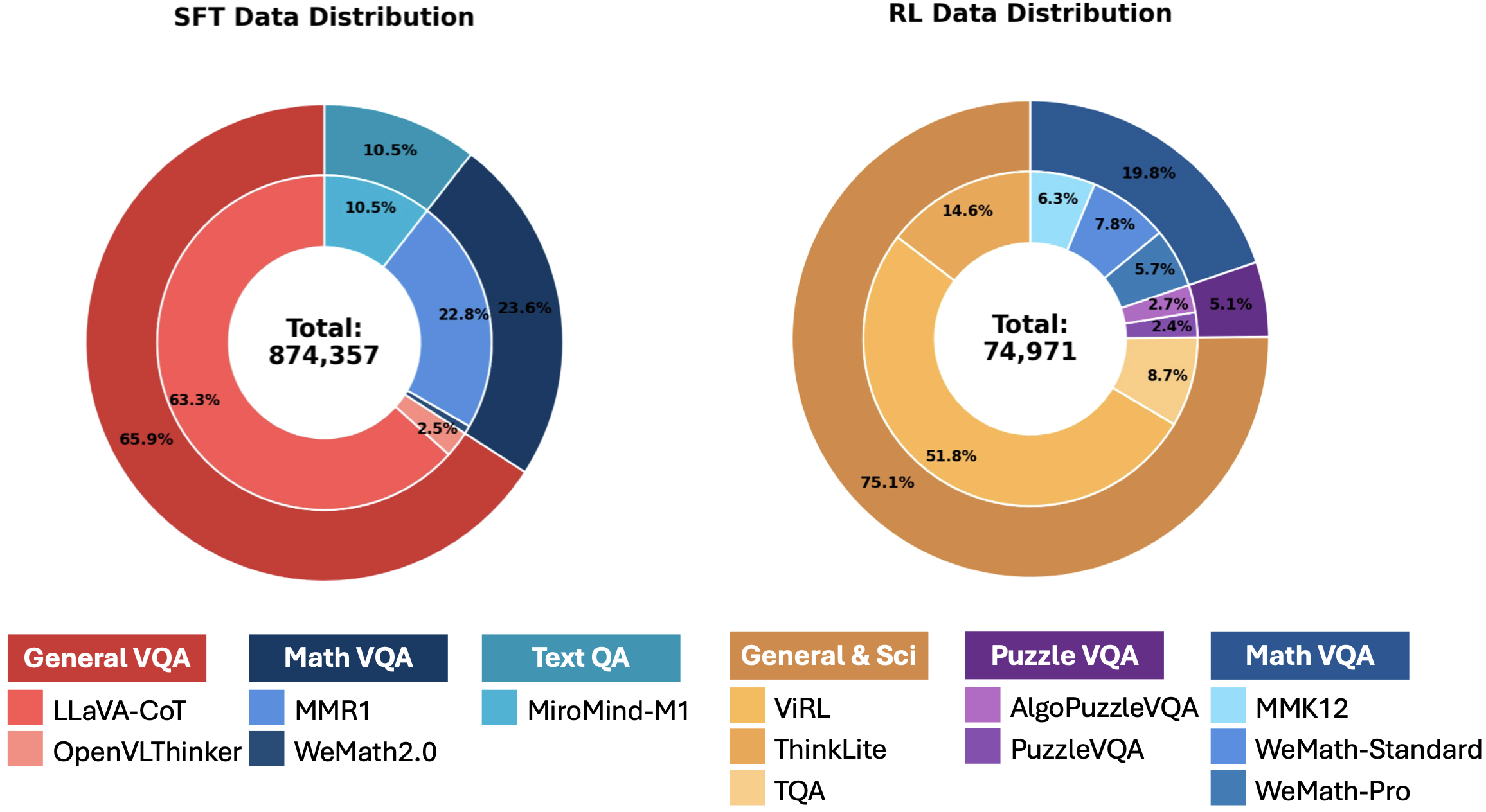
OpenMMReasoner-Data
OpenMMReasoner-Data presents two training recipes covering both the SFT and RL phases. The pipeline begins by collecting diverse data sources and selecting teacher models to generate new answer traces. During the RL phase, we explore different algorithm choices and filtering strategies, leading to our final optimized recipe.
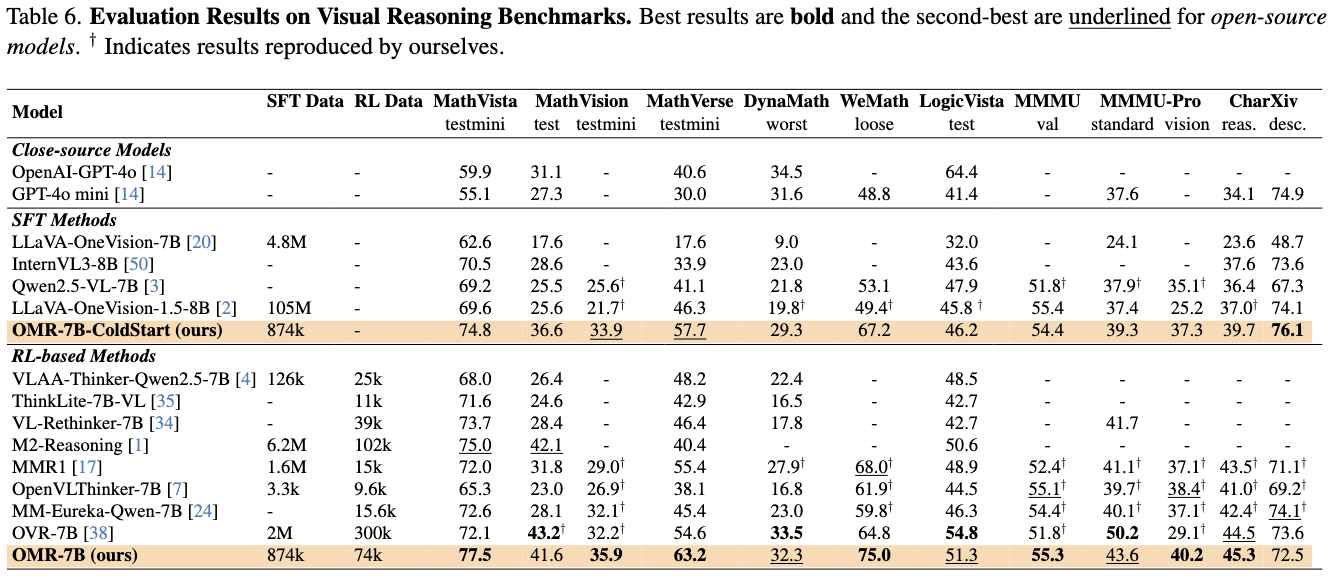
Experimental Results on Visual Reasoning Benchmarks
We evaluate our approach on a suite of public visual reasoning benchmarks. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that our training recipe not only surpasses strong baselines but also highlights the critical role of data quality and training design in shaping multimodal reasoning performance. Notably, our method achieves a 11.6% improvement over the Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct baseline across nine multimodal reasoning benchmarks, establishing a solid empirical foundation for future large-scale multimodal reasoning research.
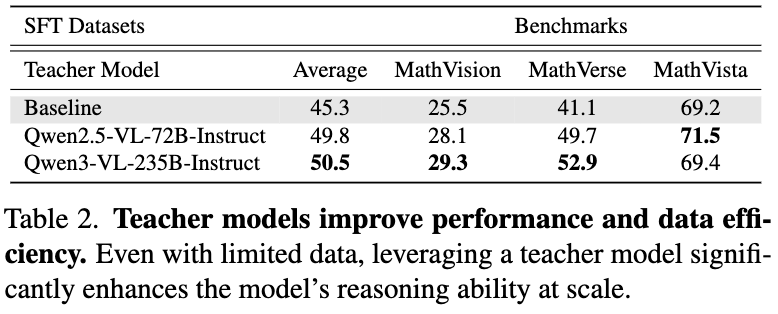
Analysis and Insights for SFT
Our Analysis and Insights for SFT are as follows:
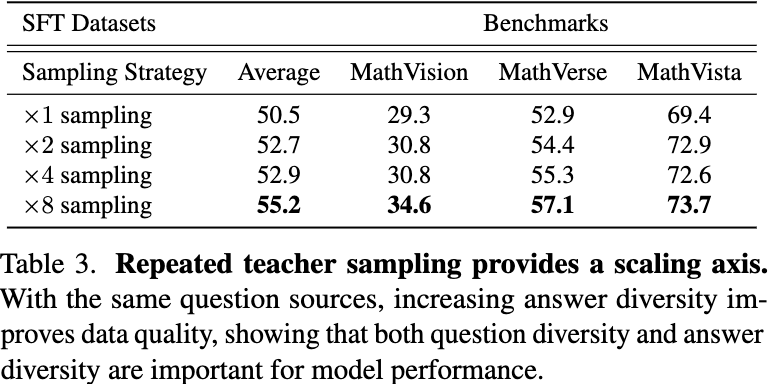
(1) Answer diversity enhances reasoning.
Increasing the diversity of generated answers consistently improves the model’s overall reasoning performance, even when using the same question sources, suggesting that exposure to varied solutions strengthens understanding.
(2) Teacher model selection is crucial.
Distilling from a strong teacher model substantially boosts the model’s reasoning ability while maintaining high data efficiency. Careful selection for teacher model directly affects the quality of the distilled dataset and the final model performance.
(3) Over-filtering reduces diversity and performance.
The best results are achieved without excessive filtering, indicating that maintaining greater answer diversity encourages more robust reasoning abilities.
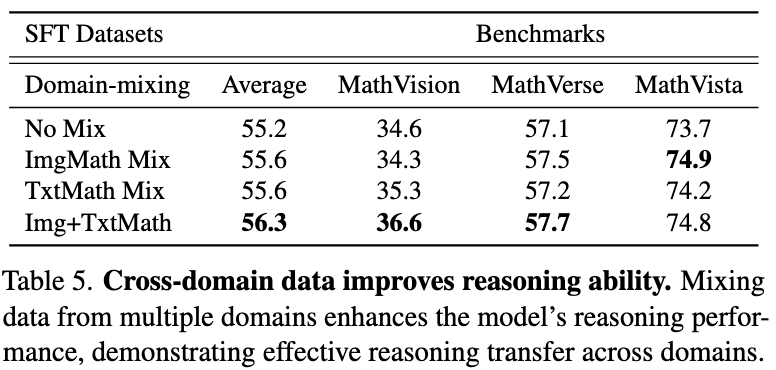
(4) Cross-domain knowledge improves generalization.
Incorporating diverse data from multiple domains consistently enhances the model’s overall reasoning capabilities across tasks.
Analysis and Insights for RL
Our Analysis and Insights for RL are as follows:
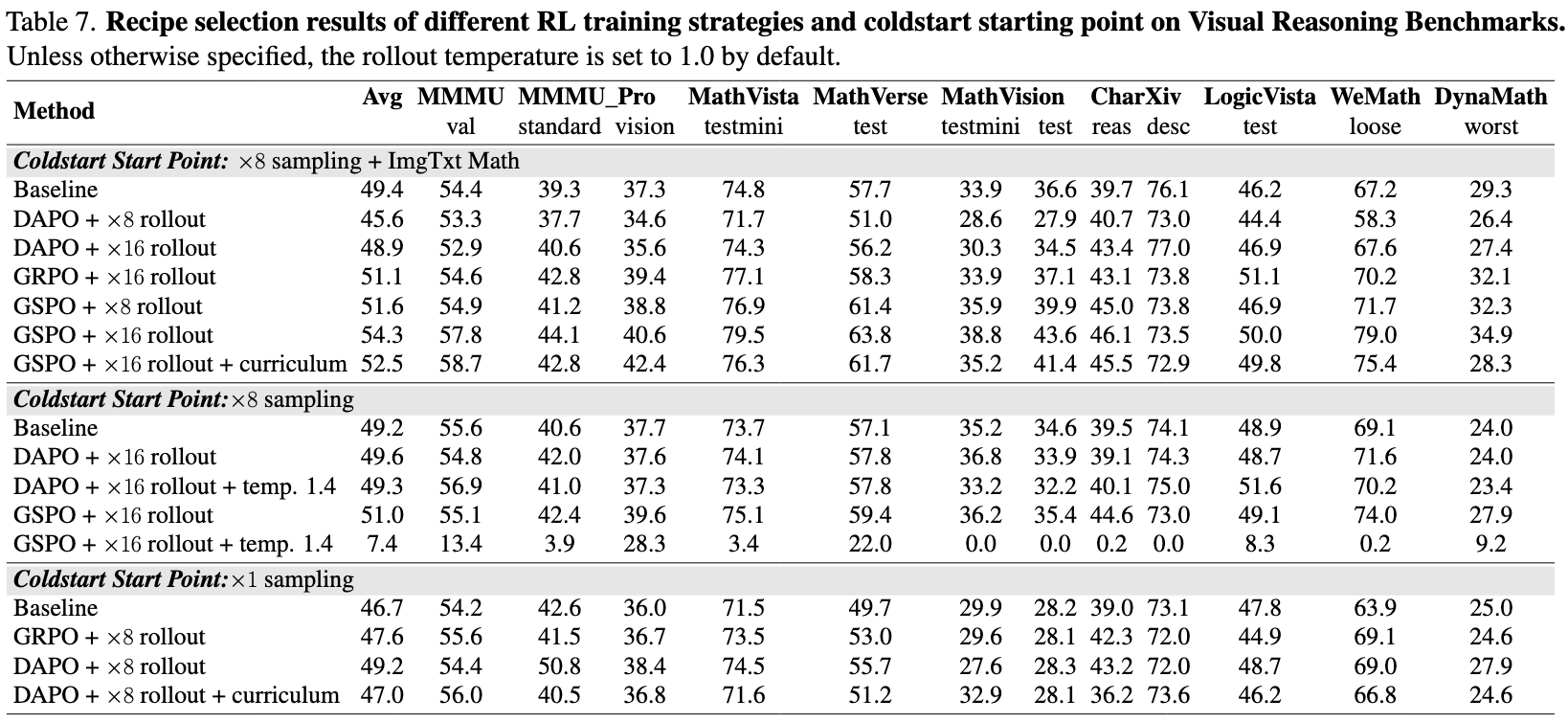
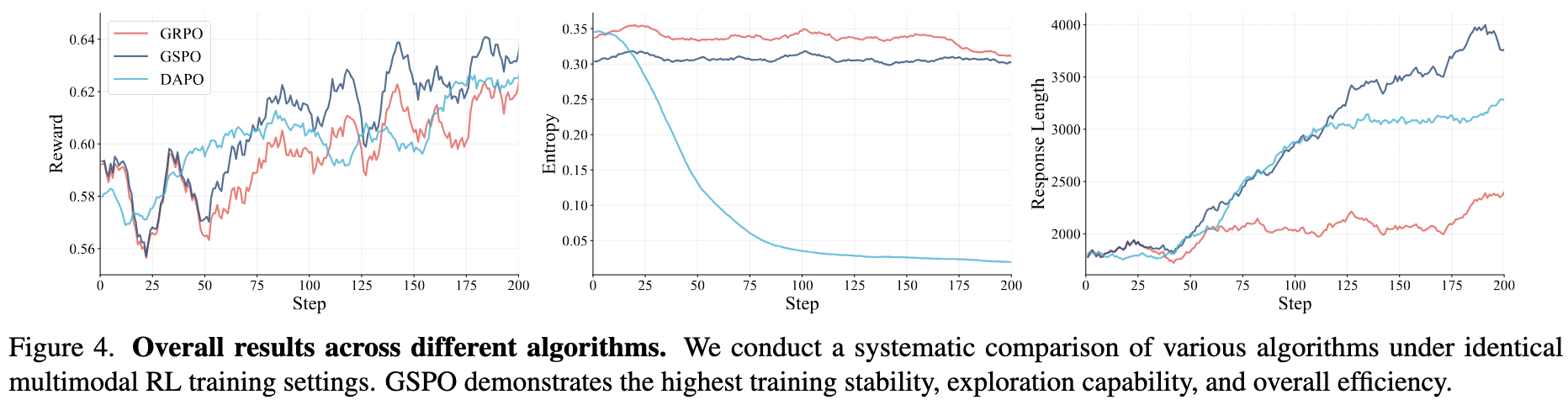
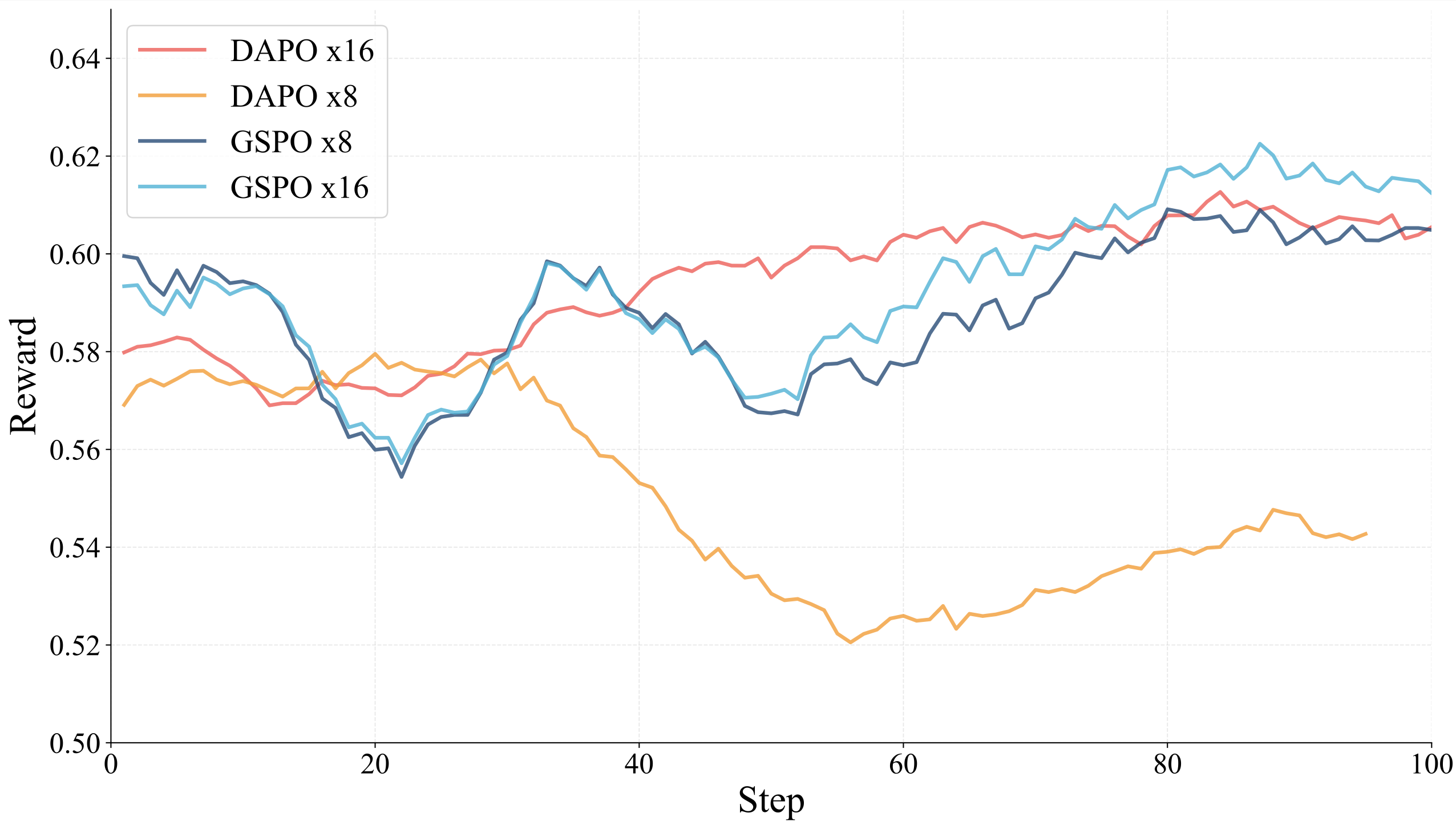
(1) GSPO outperforms other algorithms.
GSPO demonstrates superior stability and faster convergence compared to alternative methods in multimodal RL training.
(2) Token efficiency is crucial.
While increasing reasoning steps at test time can improve performance, excessive tokens reduce efficiency. Our results show that a smaller reasoning budget can achieve comparable or even better accuracy.
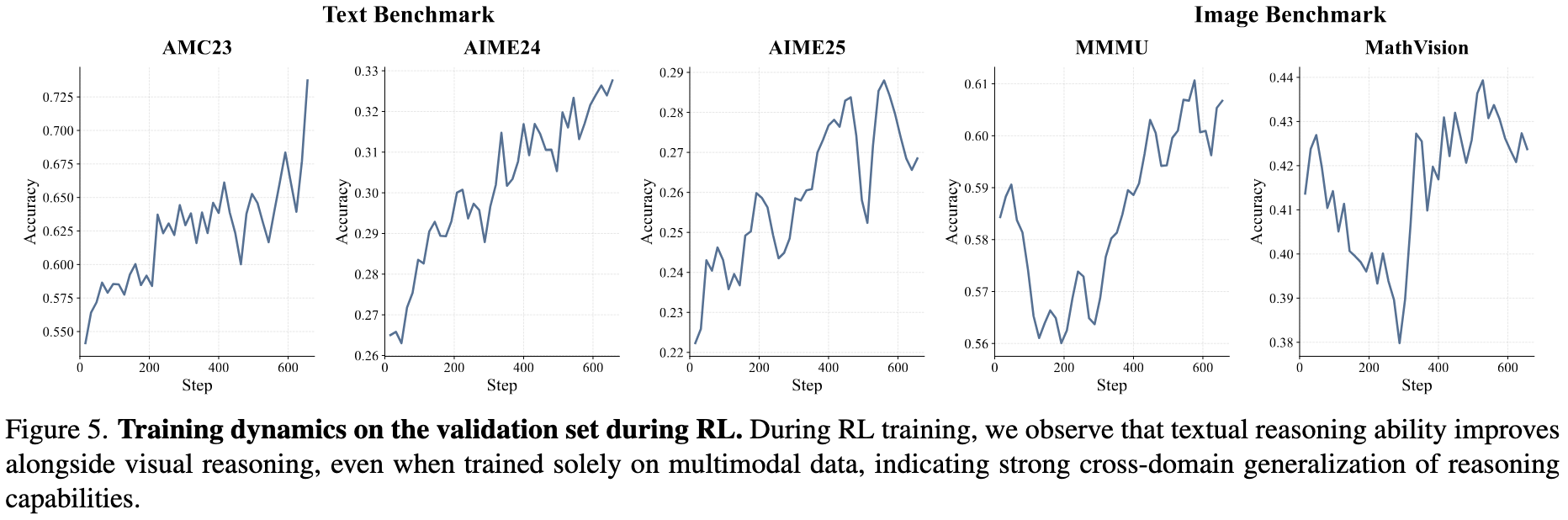
(3) Reasoning ability transfers across domains.
Gains in reasoning during training consistently translate into stronger performance across multiple domains.
Complete training and evaluation code for OpenMMReasoner
Read our paper on arXiv

