Breaking the Critic-Policy Divide
In vision-language modeling, critic models are typically trained to evaluate outputs—assigning scalar scores or pairwise preferences—rather than to generate responses. This separation from policy models, which produce the responses, is so entrenched that critics are rarely considered for direct policy use.
LLaVA-Critic-R1 challenges this convention. We propose to reorganize preference-labeled critic datasets into verifiable training signals and perform reinforcement learning directly on a base generative model, producing a multimodal critic trained to optimize preference judgments while retaining full generation ability.
Surprising Dual Excellence
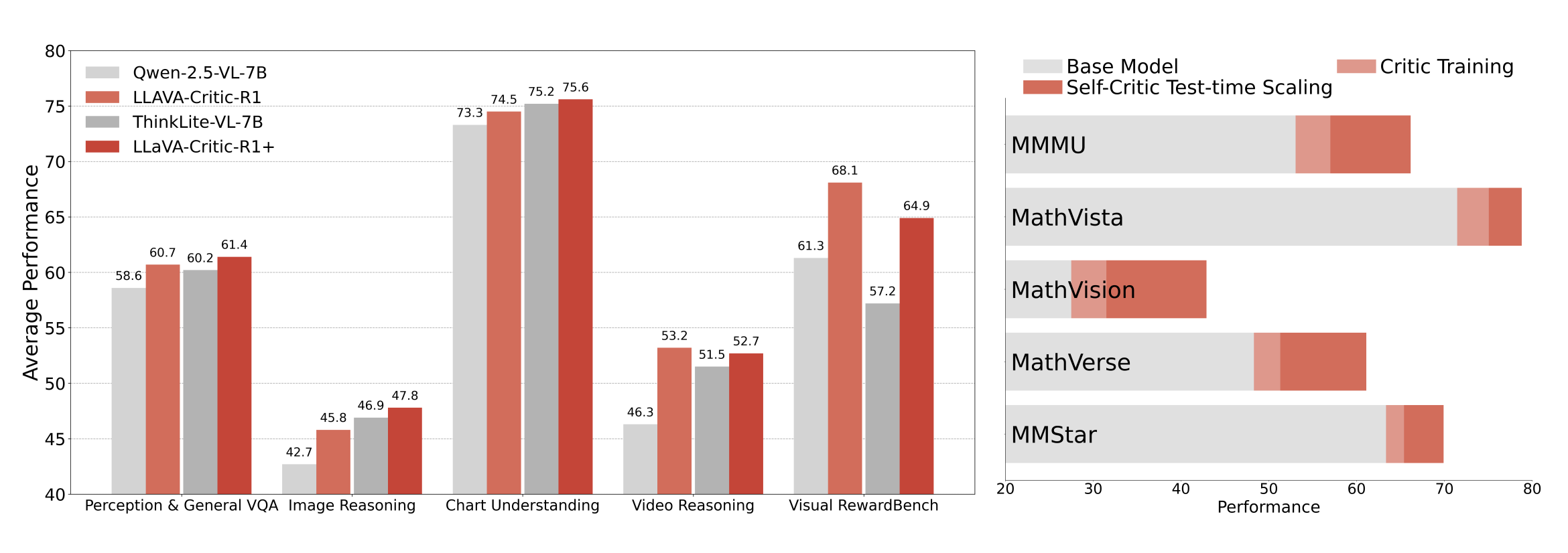
LLaVA-Critic-R1 emerges not only as a top-performing critic but also as a competitive policy model—matching or surpassing specialized reasoning VLMs trained with in-domain data across 26 visual reasoning and understanding benchmarks, with an average gain of +5.7% over its base model (Qwen-2.5-VL-7B).
Extending this approach to existing strong reasoning VLMs yields LLaVA-Critic-R1+, which further advances policy performance without sacrificing critic quality, achieving a state-of-the-art 71.9 on MMMU at the 7B scale.
Self-Critique at Test Time
The enhanced critic ability benefits inference significantly. Applying self-critique at test time yields an average +13.8% improvement on five representative reasoning tasks without additional training. This demonstrates the power of unified critic-policy models for creating self-improving systems.
Technical Innovation
Our approach centers on three key innovations:
Data Reorganization: We transform preference-labeled critic datasets into verifiable training signals suitable for reinforcement learning.
GRPO Training: We apply Group Relative Policy Optimization directly on generative models, enabling them to learn from critic data while maintaining generation capabilities.
Unified Architecture: We maintain a single model for both critic and policy functions, eliminating the traditional separation between evaluation and generation.
Model Performance
LLaVA-Critic-R1 demonstrates strong performance across diverse benchmarks:
- Visual Reasoning: Competitive performance with specialized models on complex reasoning tasks
- Critic Evaluation: Top-tier preference judgment and scalar scoring capabilities
- Generation Quality: Maintained fluency and coherence with strong instruction following
The model comes in two variants:
- LLaVA-Critic-R1: Base model trained from Qwen-2.5-VL-7B
- LLaVA-Critic-R1+: Extended approach applied to strong reasoning VLMs
Implications for the Field
Our results reveal that RL training on critic data can produce a unified model excelling at both evaluation and generation, offering a simple path toward scalable, self-improving multimodal systems. This work demonstrates that the traditional separation between critics and policies is not necessary—a single model can excel at both tasks simultaneously.