
1. Introduction
SOTA large multimodal model (LMM) architectures, such as Qwen2.5-VL, typically build on a powerful large language model (LLM) (e.g. Qwen2.5) integrated with an external Native Resolution Vision Transformer (NaViT). Such approach also presents challenges in high-resolution real-world scenarios, as these inputs are converted into enormous visual tokens, many of which are irrelevant to the downstream task. By comparison, when processing high-resolution real-world scenarios, the human visual system employs task-driven visual search strategies to ground and scrutinize critical regions of interest. Motivated by this biological mechanism, we attempt to equip LLMs with similar visual search capabilities by leveraging visual grounding to focus on key image regions.
However, empowering LMMs with such grounding-based visual reasoning capabilities is non-trivial, primarily due to the scarcity and high cost of obtaining grounding annotations for standard visual-question-answering (VQA) datasets, which are required for constructing multi-turn grounding-based conversation data for supervised fine-tuning (SFT). In this paper, we highlight that accurate grounding behavior can emerge within a reinforcement learning (RL) paradigm, even when training supervision is provided solely through a binary reward function derived from the correctness of the final answer.
To this end, we introduce Multi-turn Grounding-based Policy Optimization (MGPO), a reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm that enables LMMs to iteratively focus on key image regions by automatically cropping sub-images, based on model-predicted grounding coordinates within a multi-turn conversation framework. Given a high-resolution image and a question, the model first predicts the coordinates of key regions relevant to the query. An image cropping function is then triggered to extract and return the corresponding sub-image. In subsequent turns, the model can integrate previous in-context convesations (including both the original image and cropped sub-image) to solve the question.
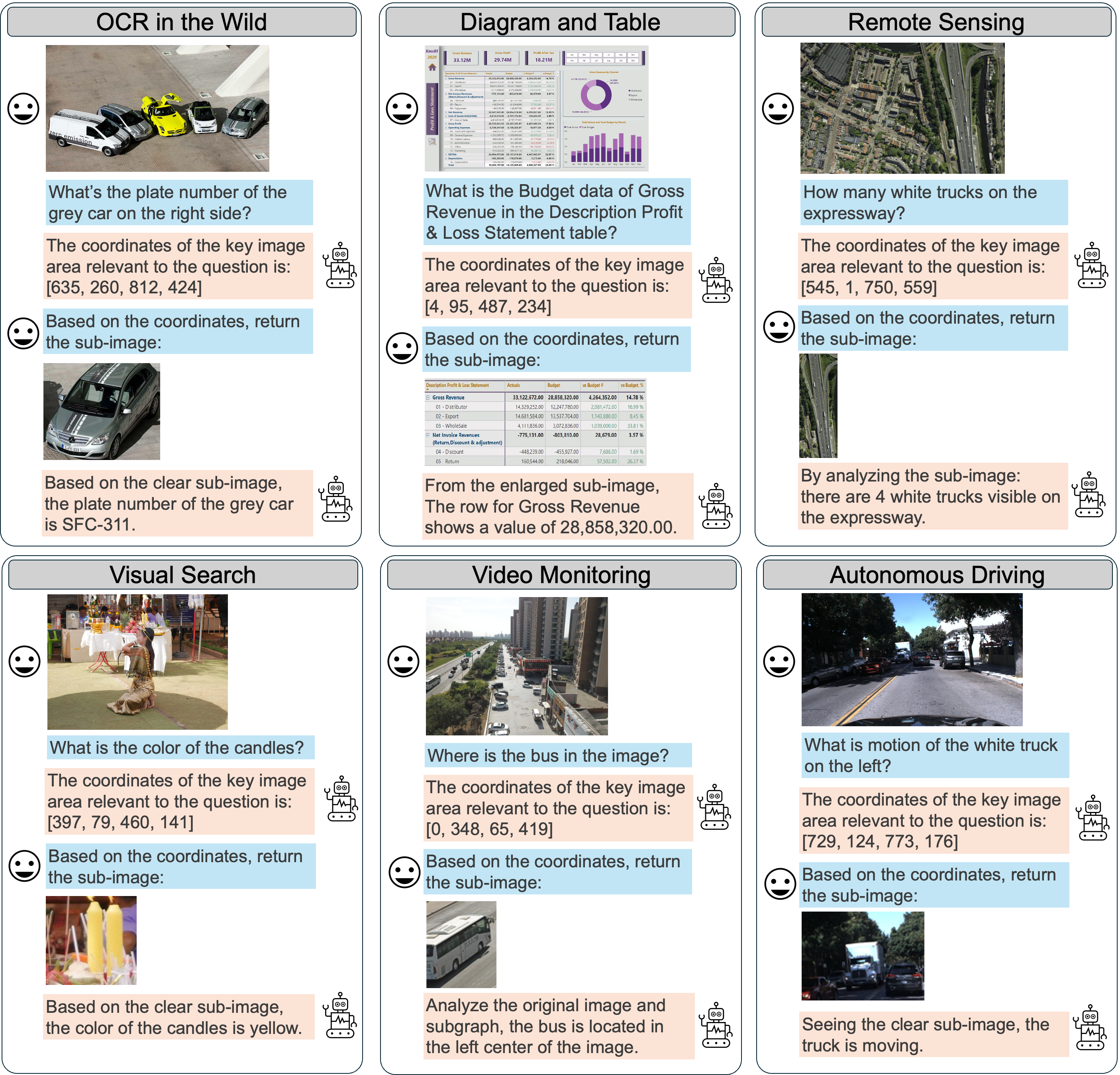
In summary, MGPO mainly offers the following advantages:
- Top-down and Interpretable Visual Reasoning. MGPO equips LMMs with a top-down, question-driven visual search mechanism for high-resolution scenarios and provides interpretable outputs that indicate which image regions are attended to throughout the reasoning process.
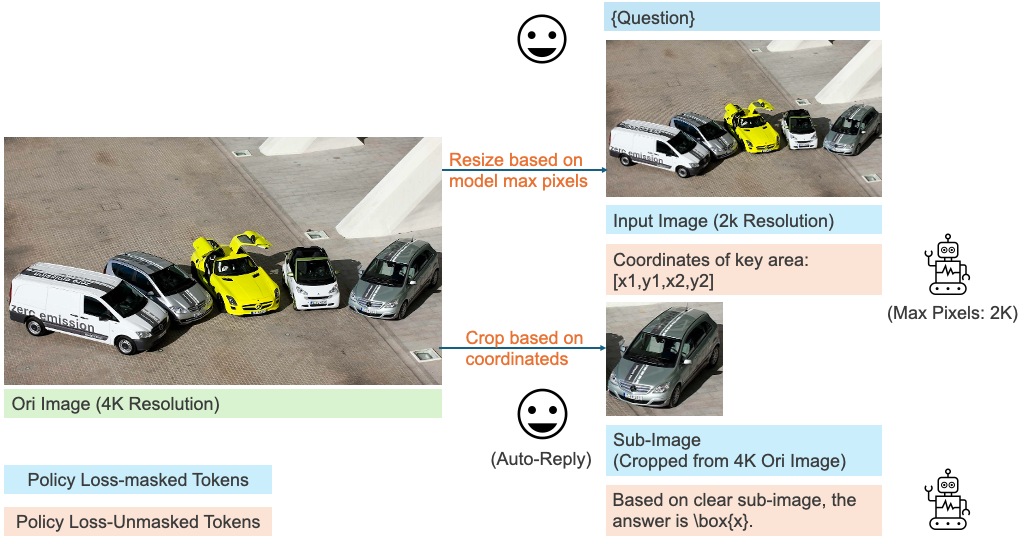
- Overcomes Maximum Pixel Constraints. MGPO can overcomes the maximum pixel limitation of LMMs. As shown in the first example of Figure 1, even when resizing a high-resolution image within pixel limits results in a blurred input, the model can still identify relevant coordinates and crop clear sub-images from the original input for further analysis.
- Without Additional Grounding Annotations. MGPO can be post-trained directly on standard VQA datasets without the need for extra grounding annotations, and experimental results demonstrate substantial improvements in intermediate grounding performance compared to GRPO
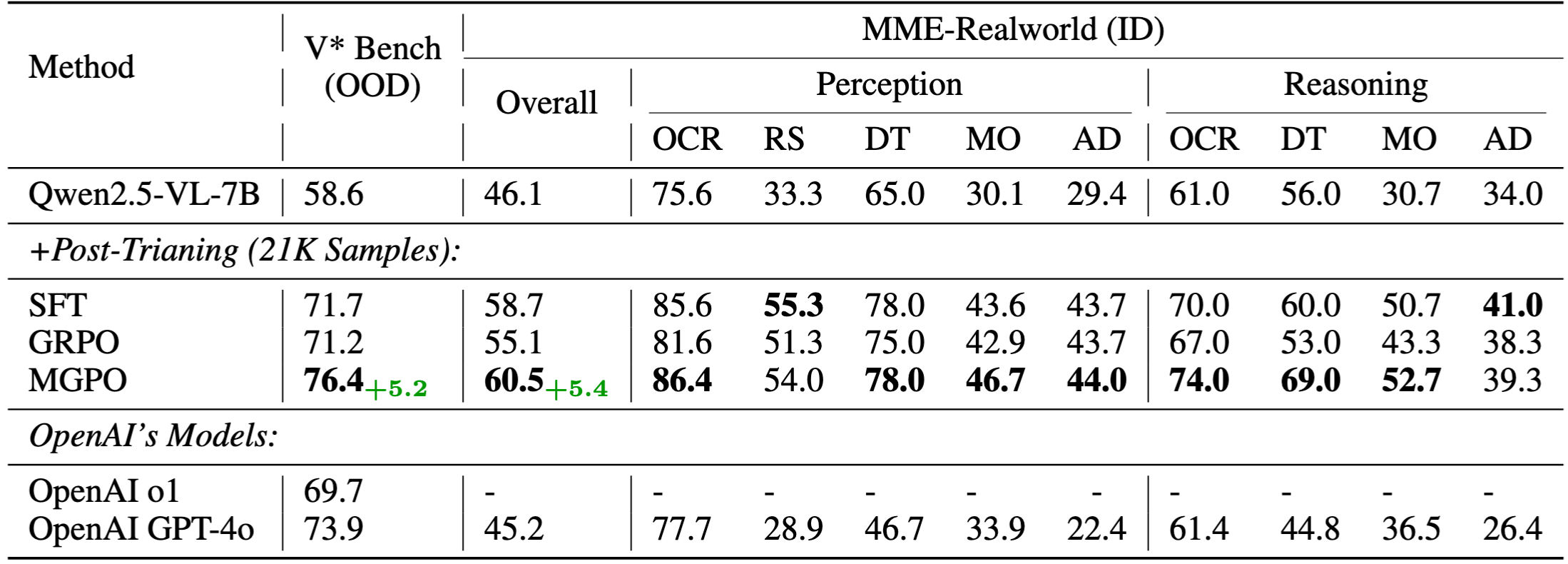
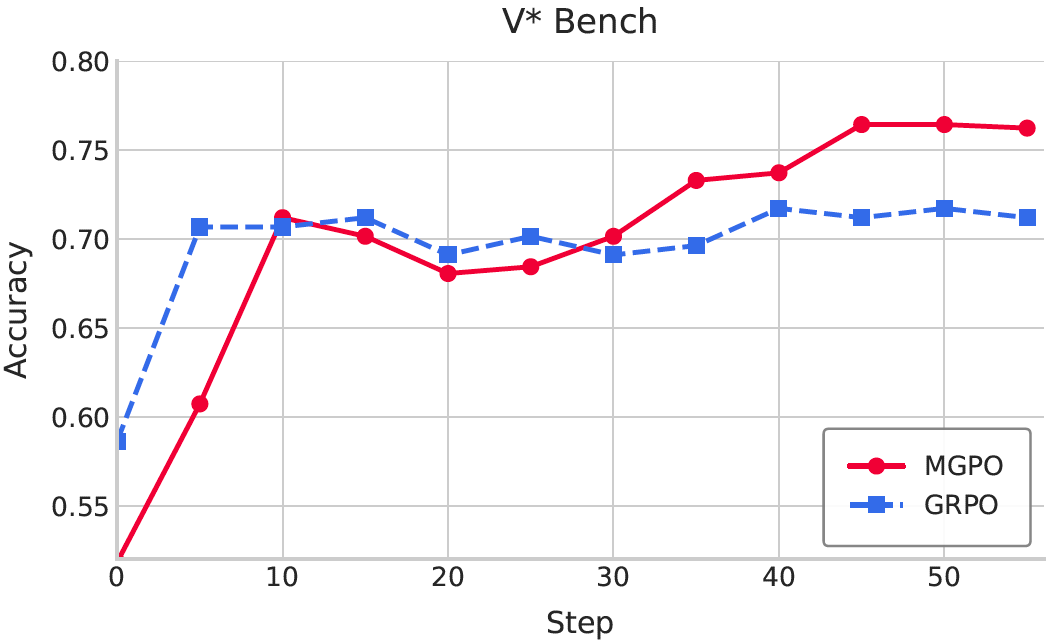
Ultimately, we utilize MGPO to post-train Qwen2.5-VL-7B using visual-question-short answering data, yet achieves strong intermediate grounding performance without requiring grounding annotations (examples shown in Figure 1). Compared to GRPO, MGPO yields a 5.4% improvement on the in-distribution MME-Realworld benchmark and a 5.2% gain on the challenging out-of-distribution V* Bench. Notably, leveraging with only 21K post-training samples, our model surpasses OpenAI’s o1 and GPT-4o models on the OOD V* Bench.
2. Multi-turn Grounding-Based RL
Figure illustrates a comparison of different post-training paradigms for LMMs. In our MGPO, the model operates over K sequential interaction, dynamically grounding and reasoning by conditioning on the full history of visual and textual context at each step.
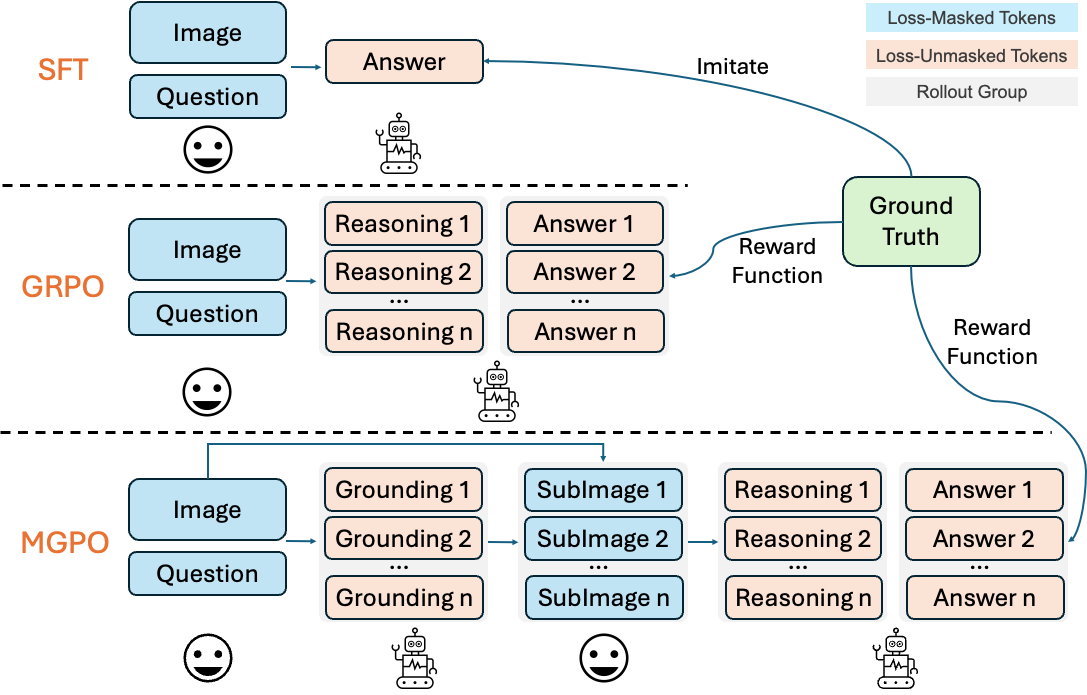
Multi-turn Template without Cold Start. In practice, we observe that LLMs struggle to autonomously generate grounding coordinates during the rollout process, which hinder effective multi-turn RL. To address this, we design a fixed two-turn dialogue template, as shown in Figure 3, to explicitly activate the model’s grounding and reasoning abilities.

Multi-turn Grounding-Based RL Process. The MGPO training process consists of the following key steps:
- Initial Grounding: Given a high-resolution image and question, the model predicts bounding box coordinates for key regions
- Image Cropping: Based on predicted coordinates, relevant sub-images are automatically cropped from the original image
- Multi-turn Reasoning: The model integrates both original and cropped images in subsequent conversation turns
- Reward Learning: Binary rewards are provided based on final answer correctness, enabling the emergence of grounding behavior through RL
3. Experimental Results
We evaluate MGPO on multiple high-resolution visual reasoning benchmarks and demonstrate significant improvements over baseline methods.
3.1 Main Results
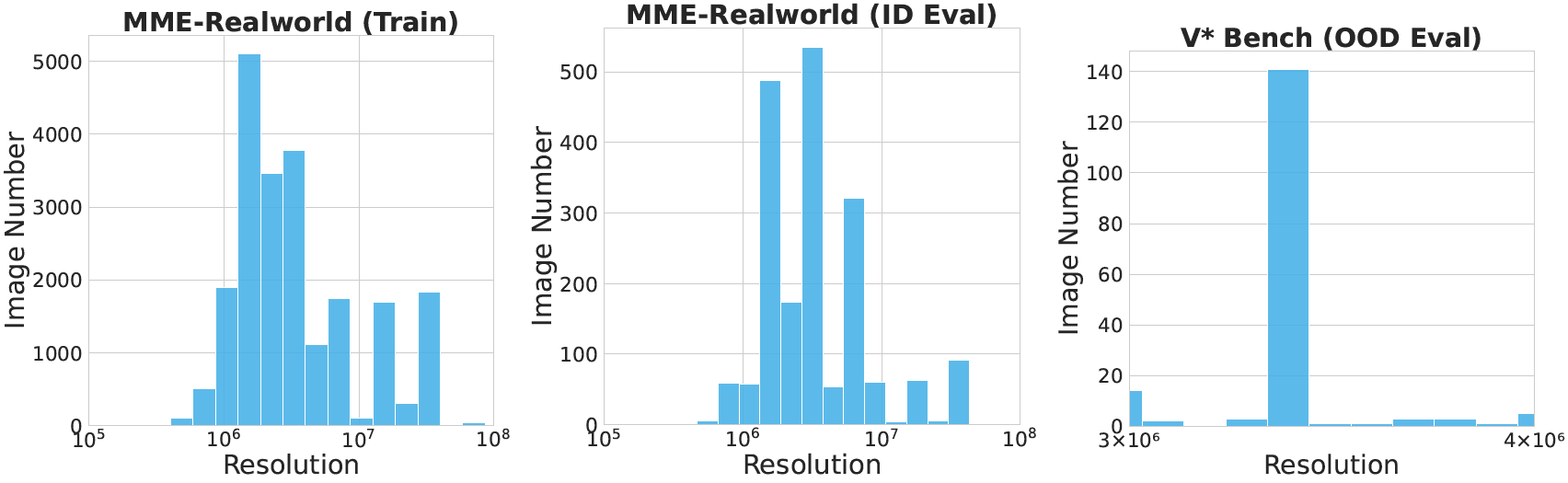
Our experimental results show that MGPO yields substantial improvements:
- 5.4% improvement on MME-Realworld benchmark compared to GRPO
- 5.2% gain on challenging out-of-distribution V* Bench
- Surpasses OpenAI’s o1 and GPT-4o models on OOD V* Bench with only 21K post-training samples
3.2 Ablation Studies
3.3 Grounding Performance Analysis
4. Additional Analysis
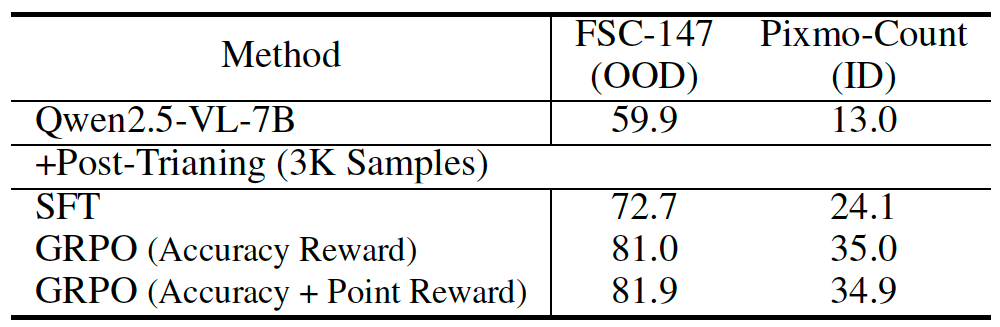
4.1 Point Counting Task
4.2 Visualization Results
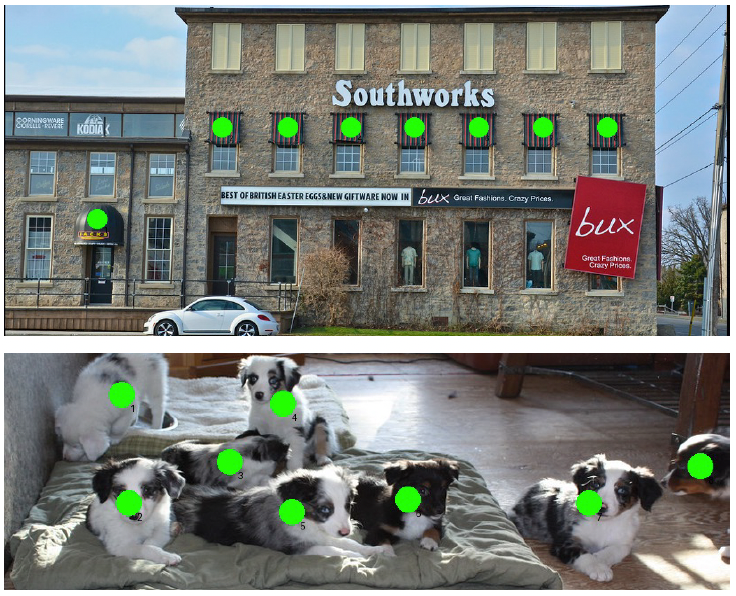

5. Limitation
All experiments of MGPO are conducted using a fixed two-turn template, rather than allowing the model to autonomously decide when to perform image cropping based on the input question, as illustrated in lasted OpenAI models such as o3 and o4-mini. This limitation stems from our observation that Qwen2.5-VL, when directly subjected to RL post-training, struggles to generate grounding coordinates without explicit prompt guidance.
Nevertheless, we believe that our trained models can be leveraged to generate high-quality chain-ofthought (CoT) data for subsequent SFT. By adopting a multi-stage training strategy that combines SFT and RL, as in DeepSeek-R1, may ultimately enable the model to autonomously decide when and how to perform grounding. We leave this direction for future work.
Appendix
