Video-MMMU asks a fundamental question: If a model ‘goes to class,’ can the model learn from the lecture and apply what it learned to MMMU-style exam problems?
🎯 Motivation
Our original goal was to build a video reasoning benchmark, motivated by the observation that the most demanding forms of reasoning arise in academic settings—for example, MMMU-style university exam questions.
Online lectures create an ideal environment for evaluating video reasoning. They effectively convey knowledge and naturally test a model’s ability to learn from video. These videos have three key attributes:
- High information density (heavy OCR/ASR signals)
- Advanced knowledge requirements (college-level knowledge)
- Temporal structure (concepts unfolding over time)
These properties make reasoning from lecture video notably harder. This leads to our core question:
When a model watches an online lecture, can it learn like a student—understand the content, acquire the knowledge, and then solve related problems?
Therefore, we introduce Video-MMMU, a video reasoning benchmark that evaluates knowledge acquisition from video.
🏆 Video-MMMU Leaderboard
| Model | Overall \ | Δknowledge | Perception | Comprehension | Adaptation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-5-thinking | 84.6 \ | — | — | — | — |
| Gemini-2.5-Pro | 83.6 \ | — | — | — | — |
| OpenAI O3 | 83.3 \ | — | — | — | — |
| Claude-3.5-Sonnet | 65.78 \ | 🟢 +11.4 | 72.00 | 69.67 | 55.67 |
| Kimi-VL-A3B-Thinking-2506 | 65.22 \ | 🟢 +3.5 | 75.00 | 66.33 | 54.33 |
| GPT-4o | 61.22 \ | 🟢 +15.6 | 66.00 | 62.00 | 55.67 |
| Qwen-2.5-VL-72B | 60.22 \ | 🟢 +9.7 | 69.33 | 61.00 | 50.33 |
See full leaderboard with 20+ models in our paper and website
📚 Overview
We introduce Video-MMMU, a multi-modal, multi-disciplinary, multi-track benchmark designed to evaluate how effectively large multimodal models (LMMs) acquire knowledge from educational videos.
1) Video: Knowledge Source
Traditional VideoQA benchmarks focus on scene understanding. Video-MMMU treats video as a source of knowledge, evaluating whether LMMs can actually learn from instructional content.
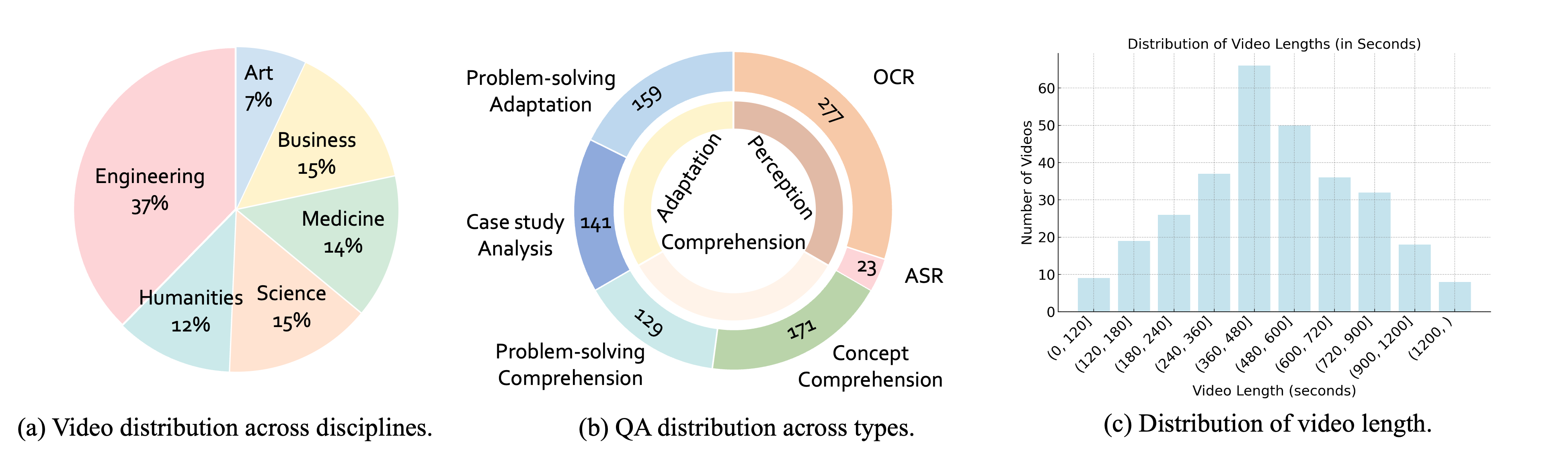
Dataset Composition:
- 300 college-level, lecture-style videos
- 30 subjects across 6 disciplines: Art, Business, Science, Medicine, Humanities, and Engineering
- High-quality educational content from university-level courses
2) QA Design: Three Stages of Knowledge Acquisition
Each video is paired with three questions, designed to reflect a progression in knowledge acquisition:
- 🔍 Perception – Identifying relevant surface information
- 🧠 Comprehension – Understanding underlying concepts or strategies
- 🎯 Adaptation – Applying learned knowledge to new scenarios

3) In-Context Knowledge Acquisition: Learning Like Humans
Humans consistently learn from the world around them. For models to operate effectively in real-world environments, the same principle should apply: they must be able to learn from the world, because unlike humans, they cannot be endlessly re-trained after deployment.
In this sense, videos provide a natural proxy for the world. For a model, the video becomes its world. The ability to learn from video therefore becomes more than a technical benchmark—it is a measure of true, dynamic intelligence. It marks the shift from simply solving a task to demonstrating the ability to learn how to solve the task.
4) Metric: From Absolute Accuracy to Learning Efficiency (Δknowledge)
A core innovation in Video-MMMU is its shift from measuring only final performance to measuring learning.
Δknowledge Formula
Δknowledge = (Acc_after_video - Acc_before_video) / (100% - Acc_before_video) × 100%
Evaluation Process
1. Initial Test: The model attempts to answer a question without seeing the video.
2. Re-Test after video viewing: We provide the corresponding lecture video. The model is asked the same question again.
3. Performance Gain: If the model succeeds after watching, it demonstrates successful knowledge acquisition from video.
This setup mirrors a human’s natural educational process:
Don't know → Learn by watching → Apply the knowledge
🔍 Key Insights

Progressive Performance Decline
Model performance decreases as cognitive demands increase. While models perform relatively better on Perception tasks, accuracy drops on Comprehension and declines further on Adaptation.
Knowledge Acquisition Challenge
The Δknowledge metric reveals a significant human–model gap:
- Humans: Substantial improvement (Δknowledge ≈ 33.1%)
- Top Models: Smaller gains (GPT-4o: 15.6%, Claude-3.5-Sonnet: 11.4%)
This highlights a current limitation: LMMs still struggle to learn from videos in the way humans do.
📊 Case Studies
Failure Case: Method Adaptation Error
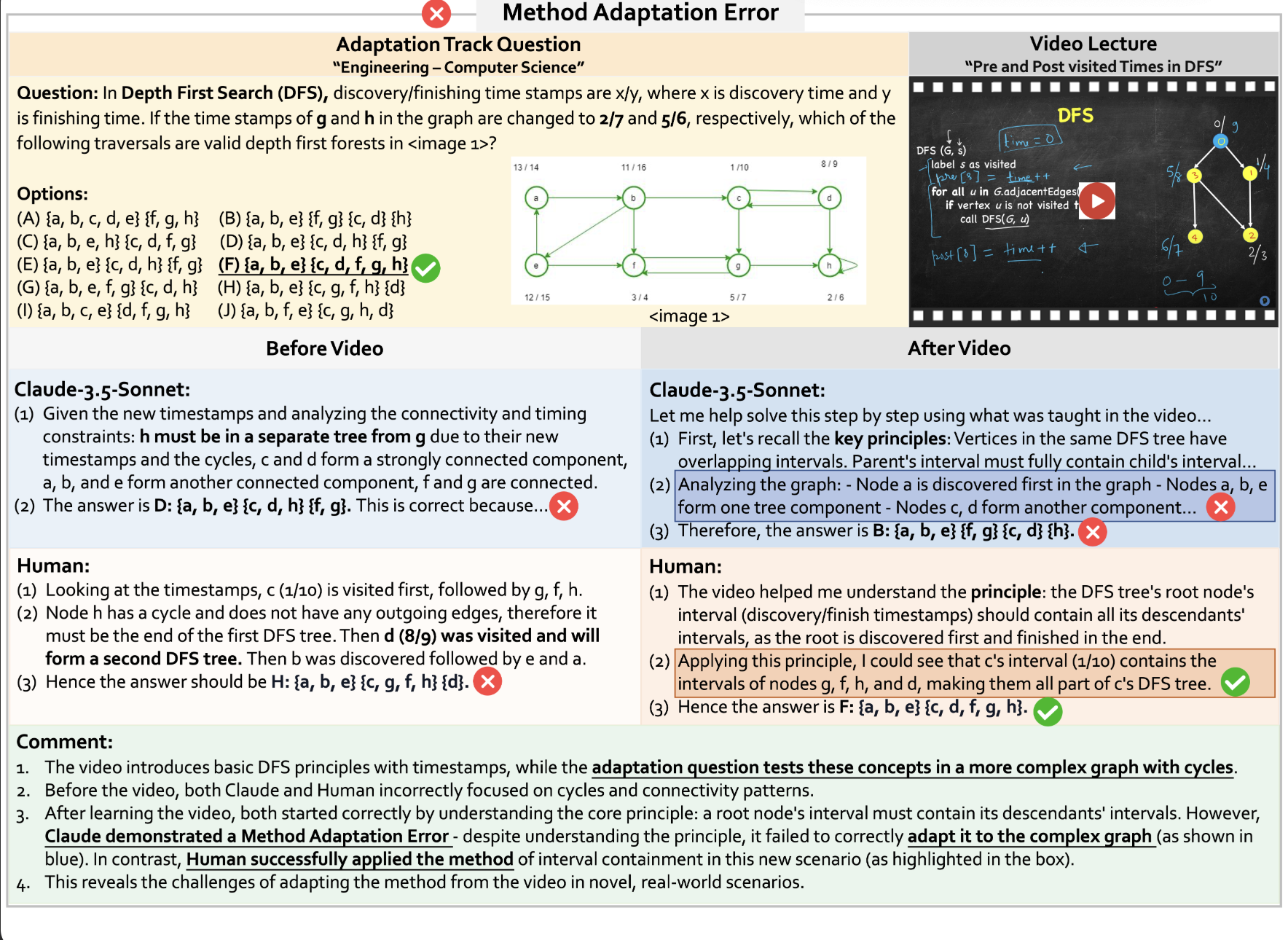
Success Case: Learning from Video
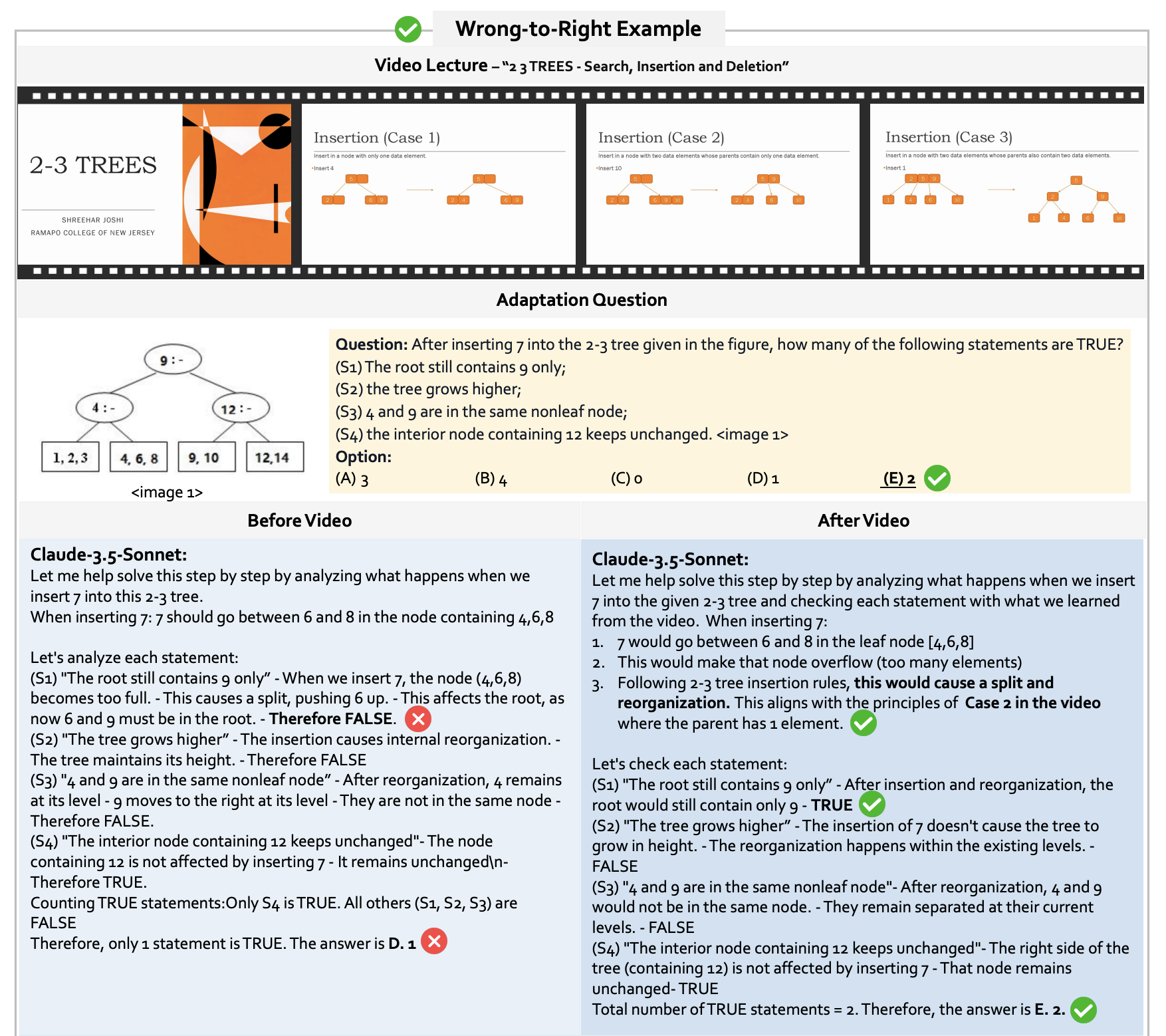
🚀 Research Impact
Paradigm Shift
Video-MMMU represents a paradigm shift from traditional video understanding to knowledge acquisition evaluation:
- From Scene Understanding to Learning - Moving beyond visual comprehension to knowledge acquisition
- From Static Evaluation to Dynamic Learning - Measuring improvement rather than just final performance
- From Task Solving to Learning Capability - Evaluating the ability to learn new skills
Implications for AI Development
- Real-World Deployment - Models must learn continuously after deployment
- Educational AI - Critical for AI tutoring and educational applications
- Knowledge Transfer - Understanding how models generalize learned concepts
- Human-AI Alignment - Bridging the gap in learning capabilities
📈 Future Directions
Benchmark Extensions
- Multimodal Knowledge Sources - Incorporating diverse educational formats
- Long-term Learning - Evaluating knowledge retention over time
- Interactive Learning - Adding feedback loops and iterative improvement
Model Development
- Learning-Optimized Architectures - Designing models specifically for knowledge acquisition
- Memory Integration - Better mechanisms for knowledge storage and retrieval
- Transfer Learning - Improving cross-domain knowledge application
🎯 Getting Started
- Download the Video-MMMU dataset from Hugging Face
- Set up the evaluation environment using our GitHub repository
- Run baseline evaluations on your models
- Analyze Δknowledge metrics to understand learning capabilities
- Compare results with our comprehensive leaderboard
Video-MMMU challenges the current state of multimodal AI by shifting focus from static performance to dynamic learning capability - a critical step toward truly intelligent and adaptive AI systems.