Overview
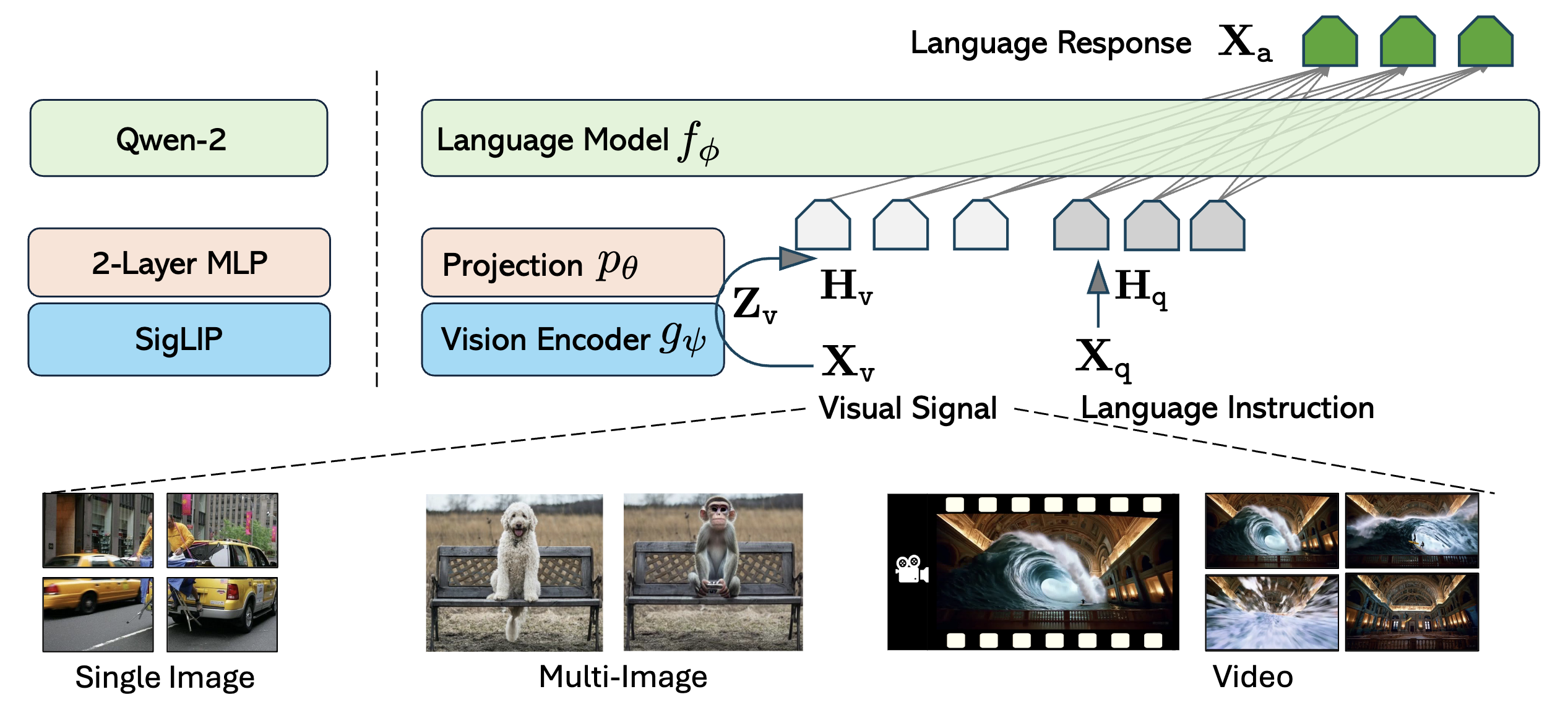
We present LLaVA-OneVision, a family of open large multimodal models (LMMs) developed by consolidating our insights into data, models, and visual representations in the LLaVA-NeXT blog series. LLaVA-OneVision is the first single model that can simultaneously push the performance boundaries of open LMMs in three important computer vision scenarios: single-image, multi-image, and video scenarios.
Key Features
Unified Architecture
LLaVA-OneVision is designed to have a similar maximum visual token count across different scenarios, enabling flexible extension to multiple visual signal types while maintaining consistent performance.
Model Sizes
- 0.5B parameters - Lightweight deployment
- 7B parameters - Balanced performance
- 72B parameters - State-of-the-art capabilities
Emerging Capabilities
The design of LLaVA-OneVision enables strong transfer learning across different modalities and scenarios, yielding impressive emerging capabilities:
1. Cross-Scenario Understanding
Seamlessly process and understand content across single images, multiple images, and videos within a unified framework.
2. Advanced Visual Analysis
- Diagram and table interpretation - Understanding complex visual structures
- Multi-screenshot interaction - Analyzing relationships across multiple screens
- Set-of-mark object referencing - Precise object identification and tracking
3. Video Capabilities
- Image-to-video generation understanding - Comprehending temporal transitions
- Video analysis and comparison - Deep understanding of video content
- Multi-camera video interpretation - Processing footage from multiple viewpoints
- Detailed video subject description - Rich, contextual video narration
Strong Transfer Learning
Importantly, the design of LLaVA-OneVision allows strong transfer learning across different modalities/scenarios. In particular, strong video understanding and cross-scenario capabilities are demonstrated through task transfer from images to videos, showcasing the model’s ability to generalize learned representations across visual domains.
Cook a SOTA model with our released training code and reproduction scripts
Access pre-trained model checkpoints in all three sizes (0.5B, 7B, 72B)
Explore comprehensive training datasets for Single-Image and OneVision stages
Try LLaVA-OneVision directly in your browser
Development Roadmap
LLaVA-OneVision represents a significant milestone in our iterative improvements through the LLaVA-NeXT series, focusing on:
- Enhanced reasoning capabilities
- Improved OCR performance
- Expanded world knowledge
- Advanced multimodal understanding
